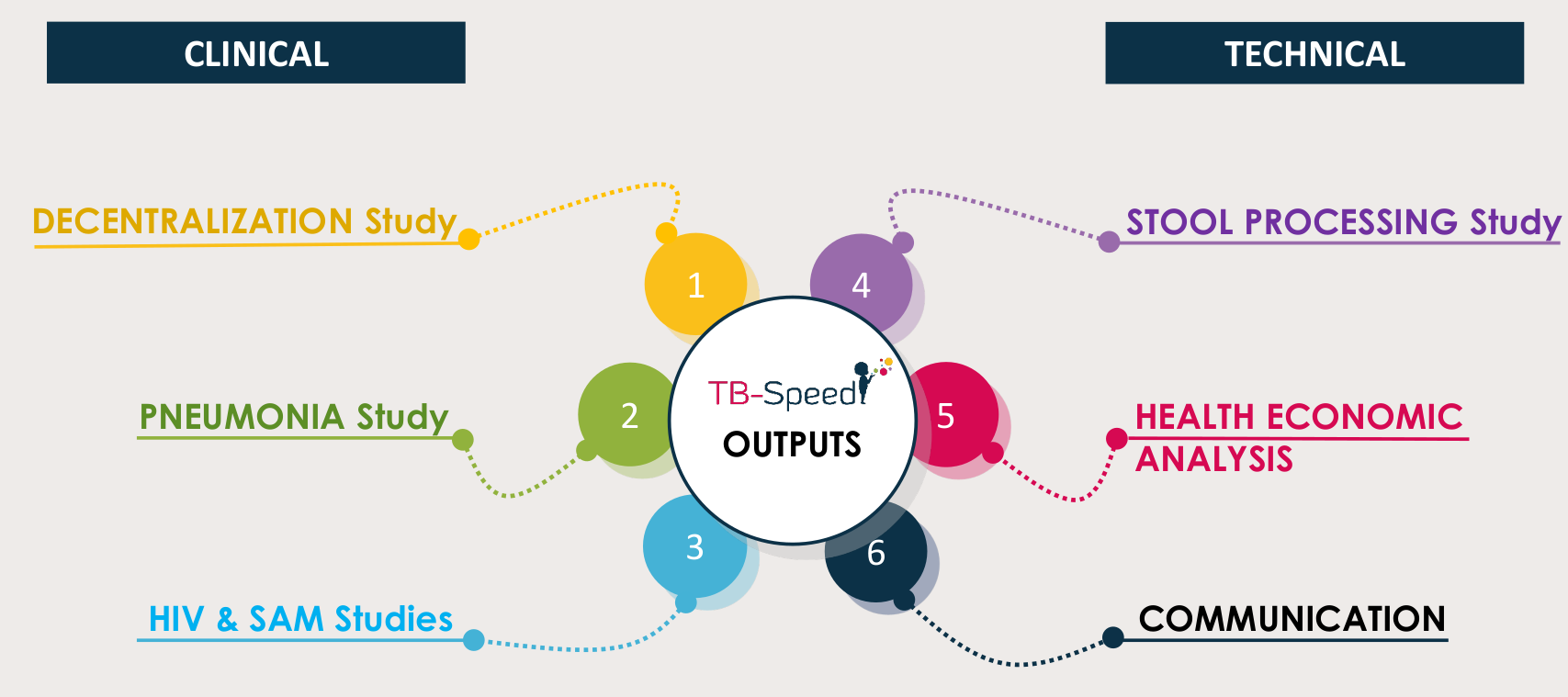
Output 1
DECENTRALIZATION STUDY
Decentralization of childhood TB diagnosis
at district health system level
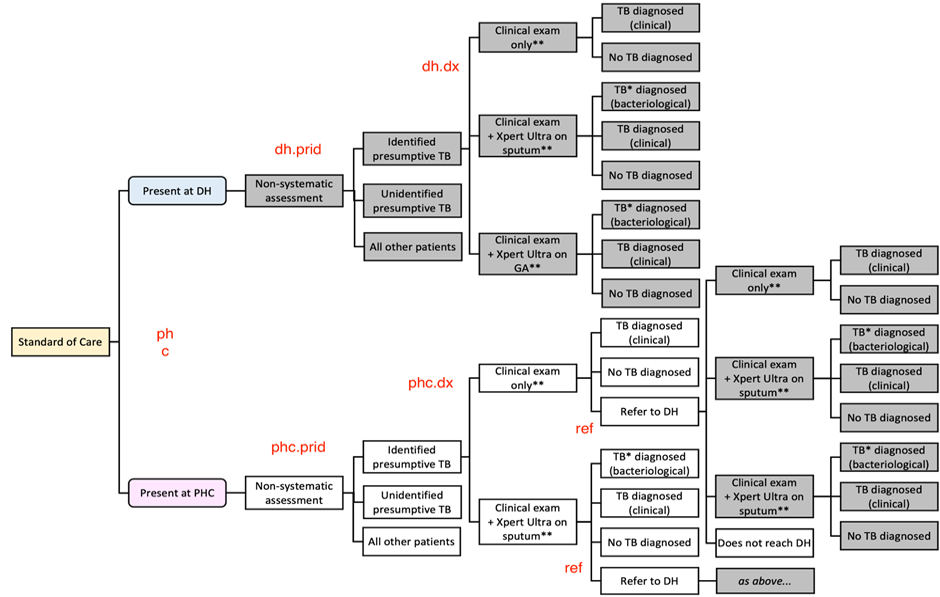
Proper TB diagnosis evaluation is rarely implemented for children at district hospital level and primary health care level in high TB-burden settings. More evidence is needed to recommend the best approach to childhood TB diagnosis in district health systems. This operational research implemented in collaboration with the National Tuberculosis Programs (NTPs) will use an innovative diagnostic approach based on Xpert MTB/RIF performed on a combination of easy to collect samples (nasopharyngeal aspirate and stool), standardized symptoms screening and chest radiograph interpretation.
Objectives
- To assess the impact on childhood TB case detection of decentralizing an innovative childhood TB diagnostic approach
- To compare the efficiency, feasibility and acceptability of two decentralization strategies





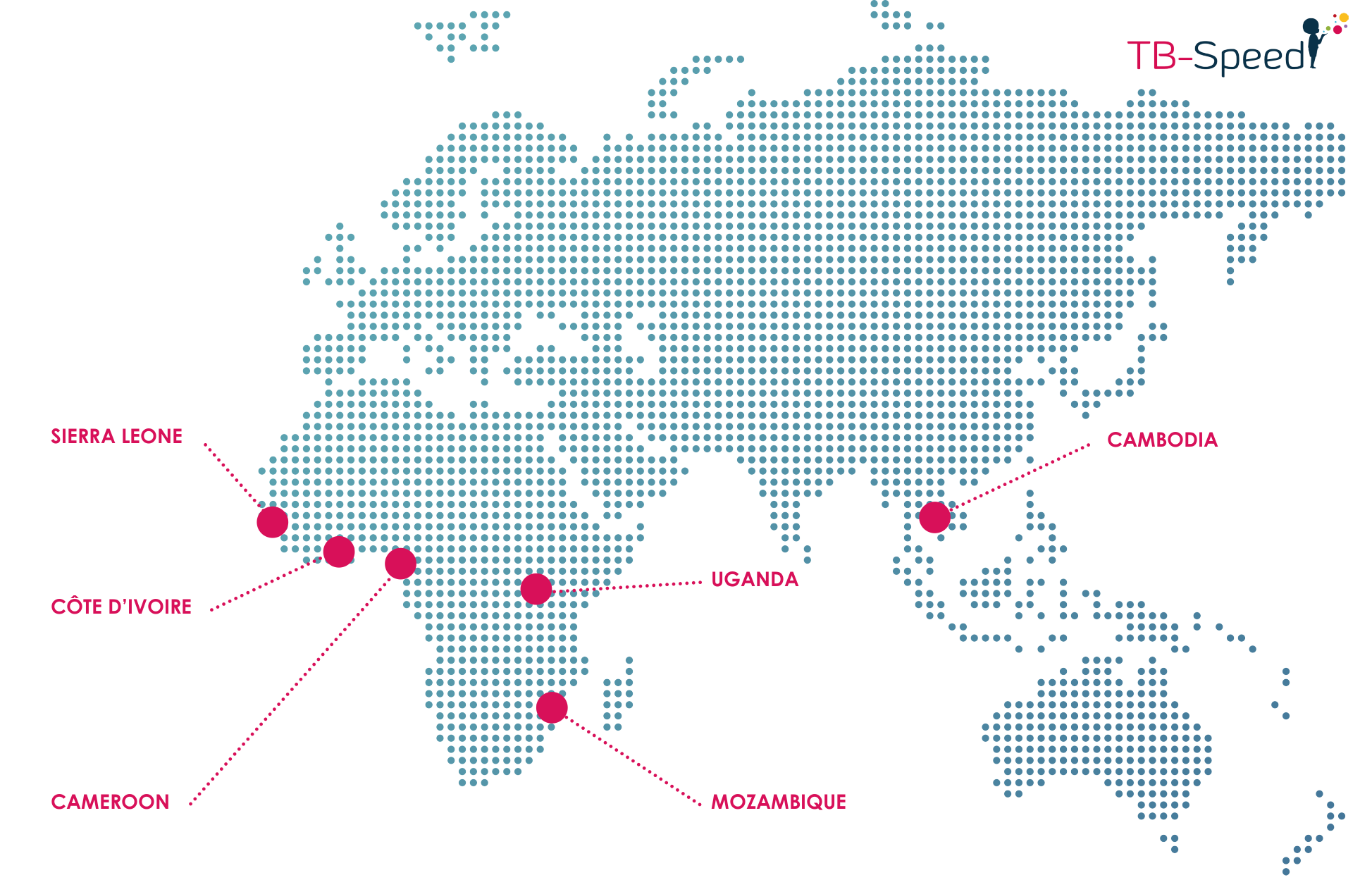
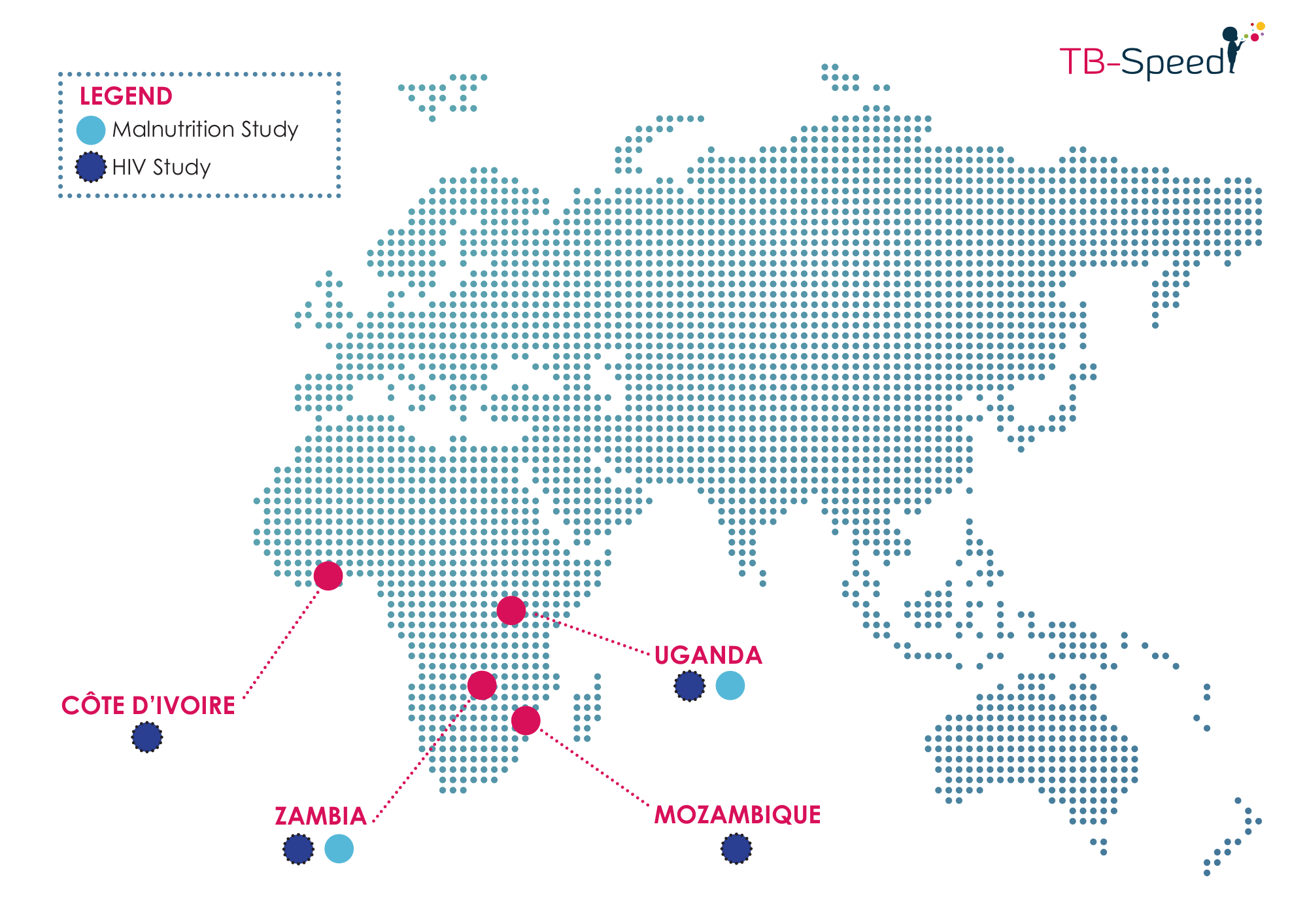
Participating countries:
Study population
- Children aged below 15 years seeking care at the district hospital and primary health care centres of selected districts.
Study intervention
- Patient level: Innovative Childhood TB diagnosis
- Systematic screening
- Clinical evaluation
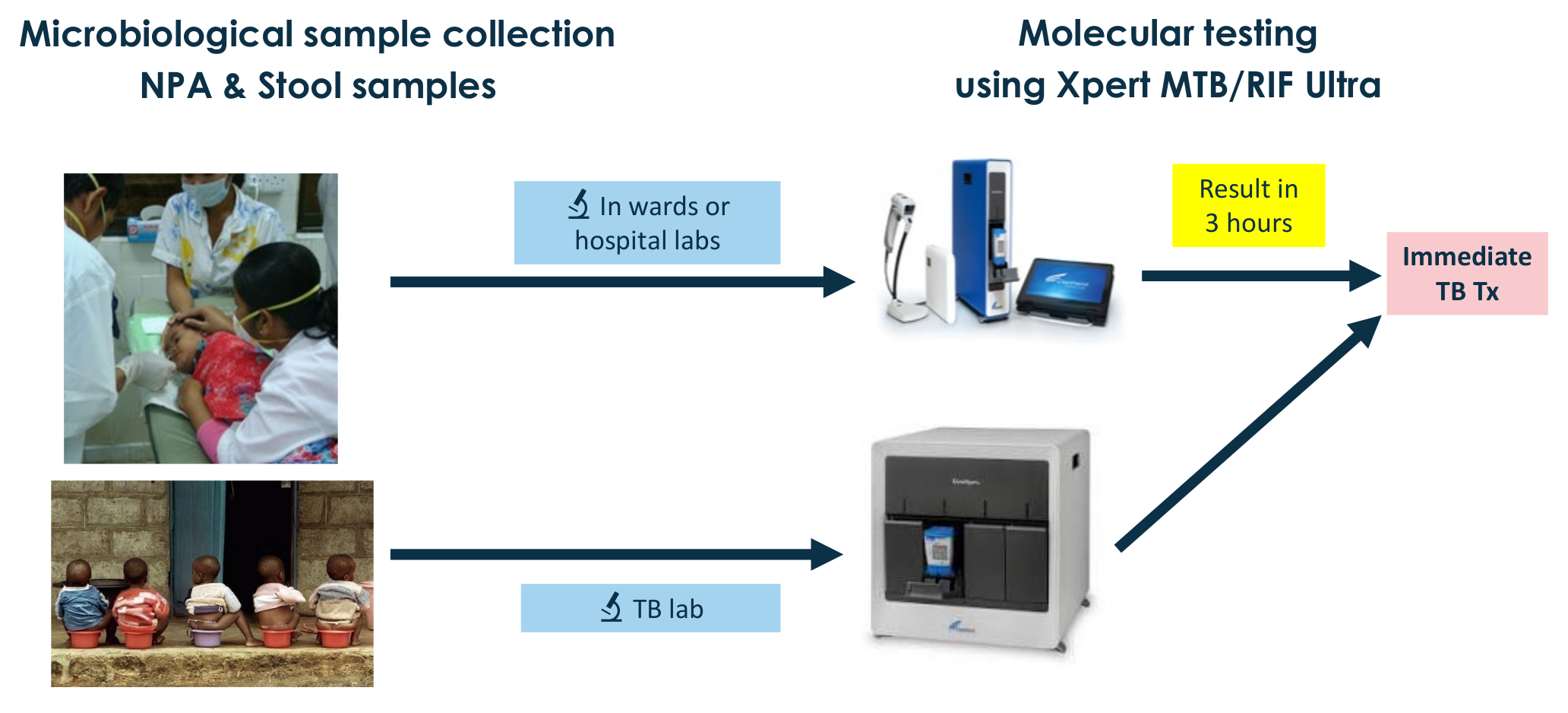
- Molecular diagnosis: Xpert Ultra on Nasopharyngeal Aspirates & stool samples
- Optimized chest X-Ray
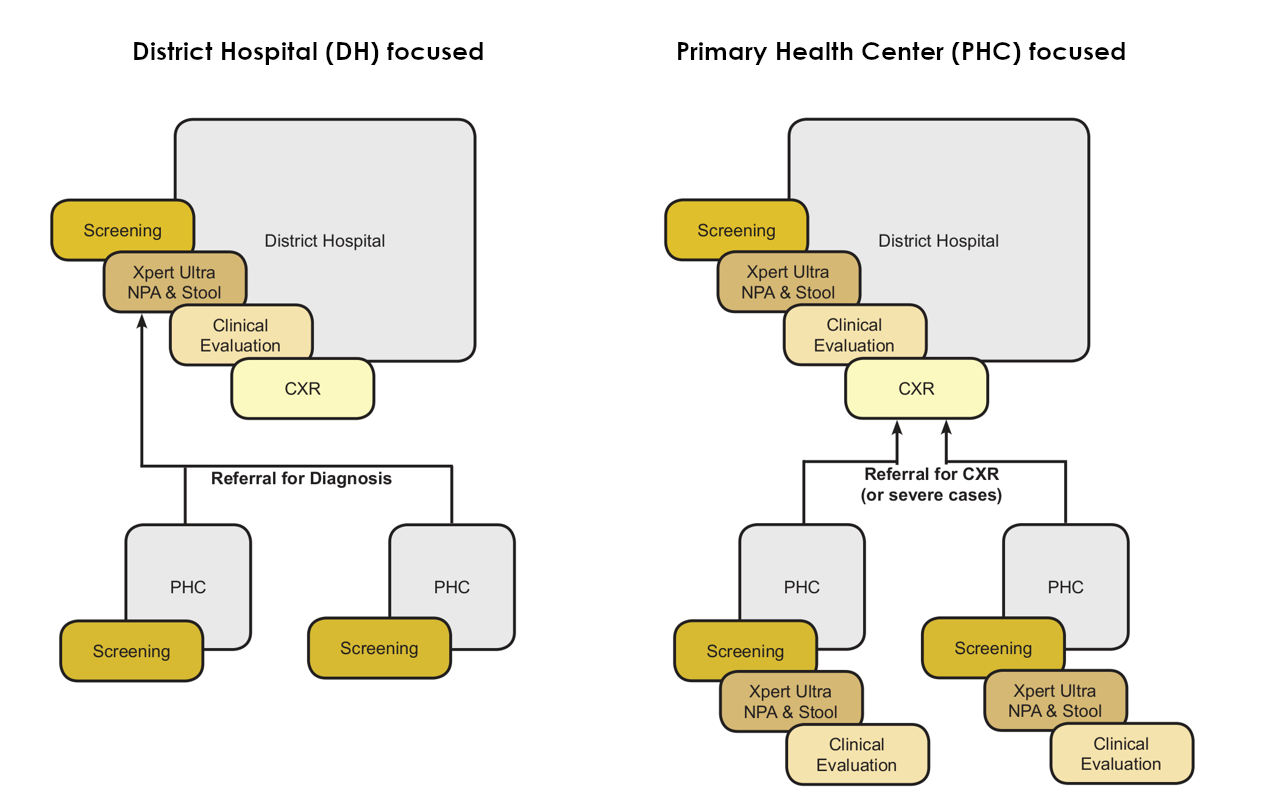
- Health System level: 2 different decentralisation strategies:
- district level decentralisation including screening of children for TB at primary health center level and reference to district hospital for microbiological, clinical and radiological diagnosis
- primary health center (PHC) decentralisation with screening, microbiological and clinical diagnosis done at PHC and reference if needed to district hospital for CXR and further investigations
Output 2
PNEUMONIA STUDY
Evaluation of an early TB detection strategy in children with severe pneumonia
TB usually presents as a chronic disease in children, with symptoms such as cough lasting for several weeks. Recent studies have shown that it can also present as a pneumonia, a rapidly progressing disease with acute symptoms including cough, fever, and shortness of breath. In children with pneumonia, tuberculosis is poorly recognized or diagnosed late, which contributes probably to increased mortality.
Objectives
- To assess the impact on 12-week mortality of adding systematic TB detection using Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra on nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPA) and stools to the WHO standard of care for children <5 years with severe pneumonia







Implementing countries
Study Population
- Children aged 2 to 59 months with WHO-defined severe pneumonia
Study intervention
- All children treated for pneumonia with the WHO standard of care (intravenous antibiotics and oxygen if needed)
- Xpert Ultra performed immediately upon admission on nasopharyngeal aspirate and stool samples
- Immediate TB treatment initiation if Ultra positive
Cluster-randomized trial, stepped wedge design
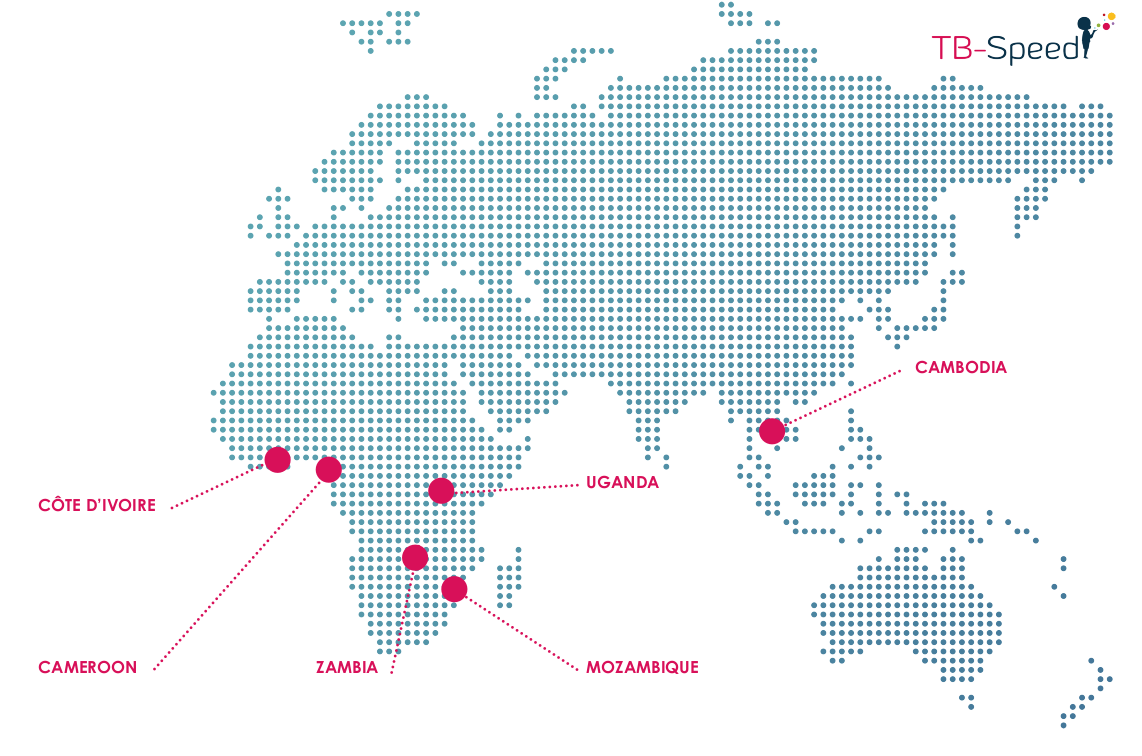
- 15 tertiary level hospitals, 6 high TB incidence countries (Côté d’Ivoire, Cameroon, Mozambique, Uganda, Zambia, and Cambodia)
- Hospitals randomly selected to switch from control to intervention every 5 week
- Randomization stratified on estimated TB incidence in the country:
- High: 100 to 300 cases/100.000 population (Côte d’Ivoire, Cameroon, Uganda)
- Very high: >300 cases/100.000 population (Mozambique, Zambia, and Cambodia)
Output 3
HIV & SAM STUDIES
Validation of diagnostic tools and algorithms
in HIV-infected children and severely malnourished children
with presumptive tuberculosis
HIV-infected children and children with severe acute malnutrition are highly vulnerable population with regards to tuberculosis. Immunodepression due to HIV or to malnutrition exposes them to a higher risk of developing tuberculosis disease and higher mortality. In these children, diagnosis of tuberculosis is challenging because they do not present a lot of symptoms, or their symptoms are hard to differentiate form other infections, especially when they are HIV-infected.
Objectives
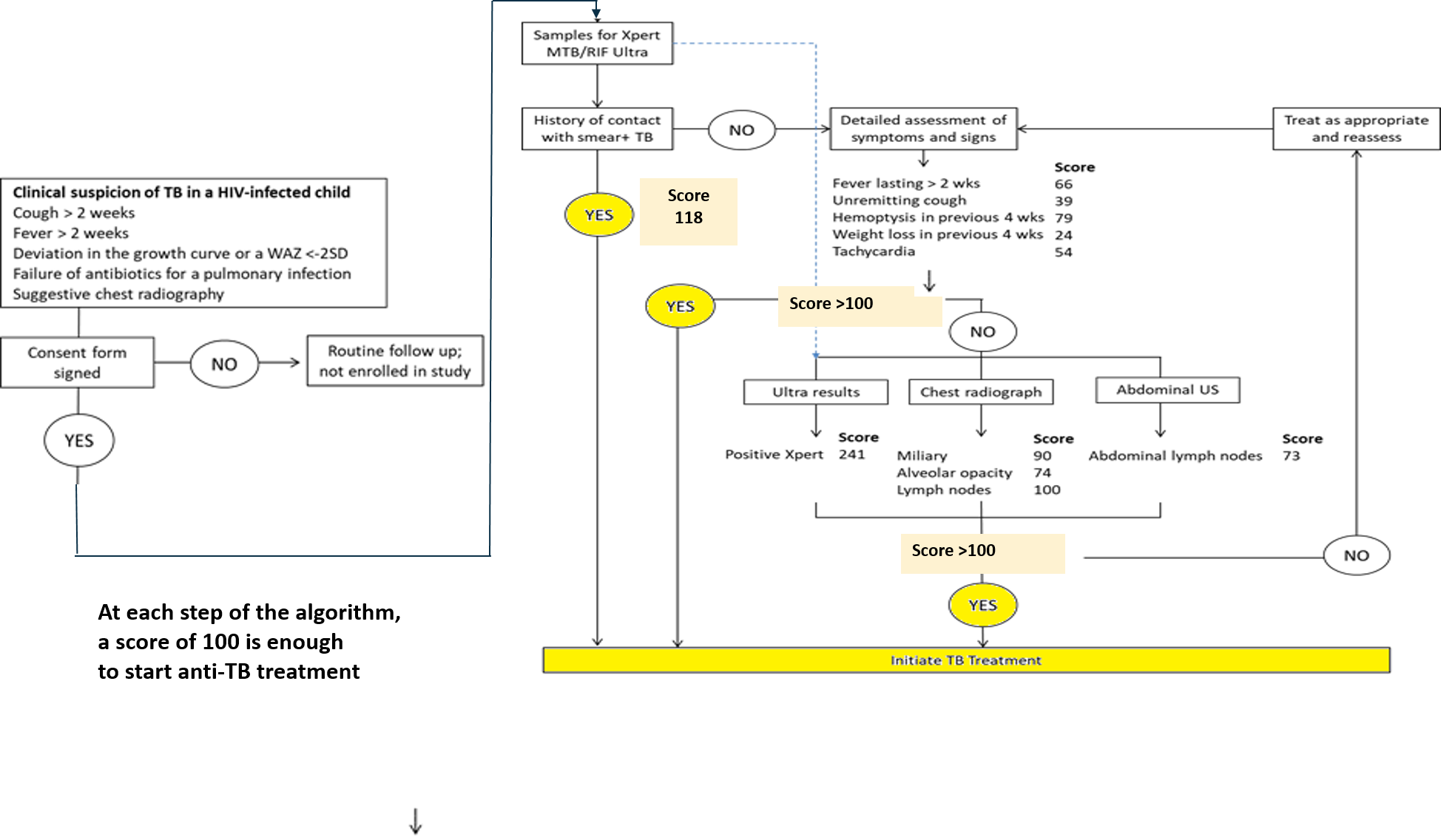
- To develop and validate specific algorithms and diagnostic tools in children with HIV and children with SAM. Algorithms are standardized decision rules for diagnosis and treatment initiation.







Implementing countries
Study Population
- 550 HIV-infected children with suspected tuberculosis
- 720 hospitalized children with severe acute malnutrition
Study intervention
- Xpert Ultra done on respiratory (NPA, sputum), and stool samples
- Chest radiography and abdominal ultrasonography
- Clinical features validated in a previous study in HIV-infected children
TB PAANTHER Therapeutic Decision Algorithm
Output 4
STOOL PROCESSING STUDY
Specimen processing and collection methods optimization
This output involves microbiological and technological optimization work to identify and test simple and affordable specimen processing and collection methods for childhood TB diagnosis that can be deployed at low health care level in resource-limited countries. Indeed, stool is a very promising sample for diagnosis of TB in children but it requires to be processed before testing with Xpert MTB/RIF assay to remove factors that inhibit the molecular technique. This processing needs to be optimised and simplified to be used at low health care level. Nasopharyngeal aspirates, another promising method for specimen collection in children, requires equipment (aspirator) and device (mucus extractor) that can be expensive and difficult to procure. Therefore more work is needed to ensure secured access of robust and affordable equipment and devices for nasopharyngeal aspirate for limited resource countries.
Objectives
- To optimize stool specimen processing for Xpert MTB/RIF testing and nasopharyngeal aspiration method for childhood TB diagnosis in resource-limited countries at low health care level.







Implementing countries
Study Population
- 550 HIV-infected children with suspected tuberculosis
- 720 hospitalized children with severe acute malnutrition
Study intervention
- Multicentric, two-stage prospective diagnostic cohort study to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra performed on stool samples collected from children with presumptive TB and processed using four different processing methods (Standard sucrose flotation method, optimized sucrose flotation method, SPK, and STEP)
Activities
- Generation of a centrifuge-free stool processing method for Xpert MTB/RIF testing
- In-vitro optimization study (spiked samples)
- In-vivo testing of different processing methods
- Optimization of nasopharyngeal aspirate sample collection
- Development of guidelines and training material for stool processing and optimized nasopharyngeal aspirate
Output 5
HEALTH ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
Cost-effectiveness of the proposed diagnostic approaches
Cost effectiveness and budget impact analyses are needed to evaluate the long-term impact of improving pediatric TB diagnostic, guide health authorities’ decisions and support the implementation of TB-speed approach in resource limited settings.
Objectives
- Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and budget impact of proposed diagnostic approaches






Output Intervention
Methods
- Development of an impact and cost-effectiveness model for pediatric TB
- Cost-effectiveness and budget impact assessment for TB-Speed
- Market analysis for pediatric TB diagnostics
- Development of a budget forecasting tool for NTPs
Output 6
COMMUNICATION
Dissemination, communication and stakeholders’ engagement
This includes communication on the project progresses, advocacy towards the relevant stakeholders, and dissemination of results to support future scaling-up.
Objectives
- To increase project visibility, involve stakeholders, raise awarenes about paediatric TB, and disseminate project results to ensure policy change







Activities
- Communication plan and stakeholder’s engagement
- Dissemination campaign targeting the scientific and health staff community
- Presentations at international conferences
- Development of educational materials